A heat exchanger is a system that transfers heat between two media of different starting temperatures. Used in both heating and cooling processes, they have a broad range of industrial applications, such as refrigeration, space heating, and air conditioning.
Shell and tube heat exchangers are the most typical type of heat exchangers used in oil processing facilities, large-scale chemical operations, and high-pressure applications. Here you’ll learn about the different types of shell and tube heat exchangers, as well as their individual components and benefits.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design
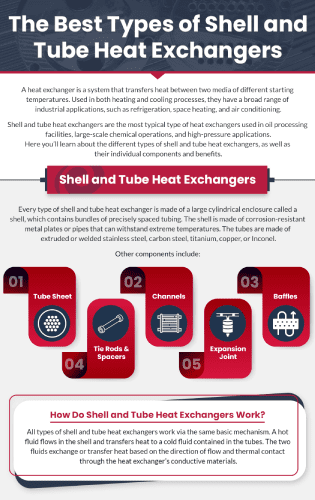
Every type of shell and tube heat exchanger is made of a large cylindrical enclosure called a shell, which contains bundles of precisely spaced tubing. The shell is made of corrosion-resistant metal plates or pipes that can withstand extreme temperatures. The tubes are made of extruded or welded stainless steel, carbon steel, titanium, copper, or Inconel.
Other components include:
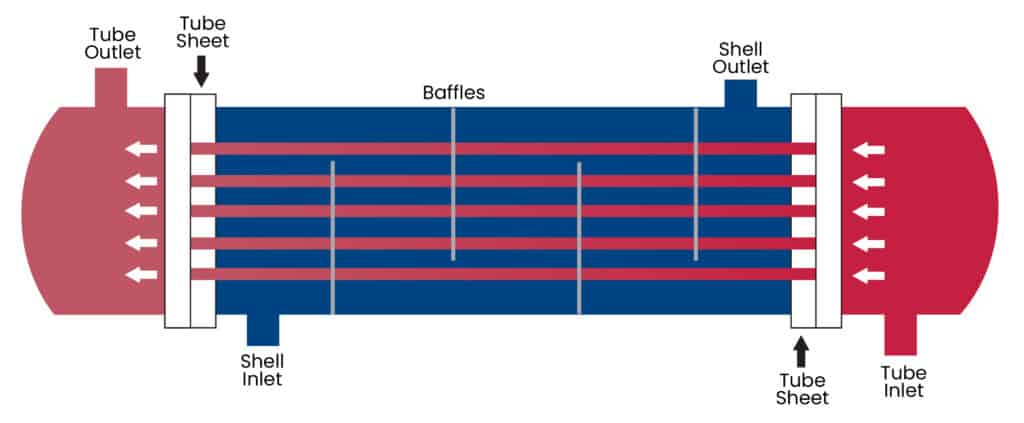
Tube sheet: The tube sheet is a plate containing holes for inserting the pipes. Its design supports the tubes on both ends of the shell.
Channels: Also called heads, channels contain fluid in the tubes and can have either bonnet-type heads for infrequent removal or removable covers for frequent removal. Channel covers are removed for inspection and maintenance purposes.
Baffles: Baffles guide the flow within the shell to boost fluid velocity, increasing the heat transfer coefficient and reducing fouling—the accumulation of materials on the heat transfer surface. Fouling can increase heat transfer resistance, thus decreasing heat exchange efficiency.
Tie rods and spacers: Tie rods and spacers maintain space between baffles while holding them in place. The appropriate number of tie rods and spacers to use depends on the shell’s diameter and the number of baffles.
Expansion joint: When transferring heat from one side of the exchanger to the other, heat exchangers are exposed to a wide range of temperatures. Expansion joints are necessary because heat exchanger materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. They prevent buckling of the tubes or shell and distortion of the nozzle connections.
How Do Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Work?
All types of shell and tube heat exchangers work via the same basic mechanism. A hot fluid flows in the shell and transfers heat to a cold fluid contained in the tubes. The two fluids exchange or transfer heat based on the direction of flow and thermal contact through the heat exchanger’s conductive materials.
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Configurations
The classification of a shell and tube heat exchanger is determined by the construction and structure of the shell as well as the type of service the unit provides.
Fixed Tube Sheet Exchanger: Two stationary tube sheets are welded directly to the shell. It is easy to clean and maintain but cannot withstand extreme temperature fluctuations without the addition of an expansion joint.
Enerquip Thermal Solutions carries Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association (TEMA) Type L, M, and N fixed tube sheet exchangers.
U-Tube Heat Exchanger: The U-tube heat exchanger is the most cost-effective version of the shell and tube design. U-tube shell and tube heat exchangers feature a tube bundle made of continuous tubes that bend into a U shape. The bundle is secured to the shell using a tube plate. The bends enable thermal expansion without the use of expansion joints, making these excellent for high-temperature fluctuations. The bent tube bundle is removable but difficult to clean mechanically.
Enerquip stocks several sanitary U-tube heat exchangers per TEMA standards.
Floating Head Heat Exchanger: The tube sheet in the floating head heat exchanger is permitted to move or float rather than being welded to the shell at the rear header end. This allows for thermal expansion and removal of the tube bundle for cleaning. This type of shell and tube heat exchanger is suitable for processes involving high temperatures and pressures, but it is more expensive than fixed tube sheet heat exchangers.
Enerquip carries TEMA Type W, P, S, and T floating head heat exchangers.
Advantages of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Used in a variety of industries and applications, shell and tube heat exchangers are highly versatile pieces of equipment. Benefits include:
- Cost-effective
- Handles a wide range of temperatures and pressures
- Adjustable design allows for thermal expansion
- Minimal pressure loss
- Handles flammable or toxic fluids
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers from Enerquip
Given the wide range of applications and types of shell and tube heat exchangers, selecting the right model for your application is key to reaping every possible benefit. Your specific technical requirements determine the ideal type of shell and tube heat exchanger for your application. Enerquip is a leading shell and tube heat exchanger manufacturer with over 35 years of extensive industry experience.
Request a quote or contact us today for more information.